Riggins Forest Health Research Lab
Welcome to the webpage for the Forest Health Research Lab at Mississippi State University, led by Dr. John J. Riggins

Meet the Team
Current Members
John J. Riggins, Ph. D.
Dr. Riggins is originally from Nebraska. He received a B.S. and M.S. in Biology from the University of Nebraska at Kearney. During his time there he studied tiger beetles, carrion beetles, and below-ground invertebrates of wet meadows along the Platte River. He received a Ph.D. in Forest Entomology under Dr. Fred Stephen at the University of Arkansas in 2008. His research in Arkansas used traditional field ecology and modern geospatial techniques to investigate an outbreak of the red oak borer in the Ozark mountains. His current research investigates how disturbances and symbioses influence forest biogeochemistry. In his spare time, Dr. Riggins spends as much time as possible with his wife, Erika and his children Ian, Isaac, Zoey, and Max. He also enjoys hunting, fishing, camping, hiking, and reading.
John W. Thomason

Tianze "Jack" Xue
Jack was born in Northern part of China. He received his B.S. in Entomology from Purdue University. Under the stewardship of Dr. Anthony Cognato at Michigan State University, Jack obtained his M.S. degree in Entomology in 2024. His project there was to figure out the taxonomic relationship of a new established Scolytinae genus. At Mississippi State University, Jack will be studying interactions between insects and pine needle blight pathogens in Mississippi. He has a strong intertest in coleopteran taxonomy and is a beetle collecting hobbyist.



Dr. Davide Nardi
Davide Nardi received his PhD in Crop Science at the University of Padua, Italy in 2023 with a PhD dissertation titled “ Multi-taxa responses to forest disturbances through a multi-disciplinary approach ”. During the research activity he has often adopted a multidisciplinary approach, acquiring expertise in community ecology, network approach, spatial statistics, remote sensing, and metabarcoding analysis. His main research interest is insect ecology in the forest environment. He is also a spider specialist with a strong focus on spider ecology.
Natalie A. Clay, Ph.D.
Natalie received her Ph.D. from the University of Oklahoma Biology Department in 2013 in the Ecology and Evolutionary Biology program after earning a B.A. magna cum laude double majoring in biology and art from Colby College. Natalie brought a wealth of knowledge in ecosystem ecology, nutritional ecology, and community ecology. Dr. Clay is an Associate Professor of Forest Health at University of Arkansas, Fayetteville .
Dr. John Formby
Dissertation Title: Invasion potential and overwintering biology of the Redbay Ambrosia Beetle (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in the United StatesJohn graduated in 2016. He is now a small business owner in New Mexico.

Dr. Nathan Little
Dissertation Title: Implications for the detection, utilization, and degradation of bark beetle-attacked southern pines by subterranean termites. Nathan graduated in spring of 2013. He is now a research entomologist with the Stoneville, MS. USDA ARS .
Kristy McAndrew, Ph.D.
Kristy graduated in spring of 2021 (congratulations!!) and is now an Extension Instructor in Forestry Dept. at Mississippi State University.

Matthew Thorn
Thesis Title: Recreational firewood movement as a vector of non-native woodborers in MississippiMatt graduated in 2017, and currently works for the Columbus Air Force Base. as the Natural Resource Manager.

Dr. Kevin Chase
Thesis Title: Forest stand preference of Sirex nigricornis, and Sirex noctilio hazard in the southeastern United States.Kevin graduated in 2013, and is currently a research entomologist with Bartlett Tree Experts at their headquarters in Charlotte, North Carolina.

Nathan Blount
Thesis Title: Field survey of native and non-native subterranean termites in southeastern United States forests .Nathan Graduated in Spring of 2012, and is currently a Wildlife Biologist for Mississippi Department of Wildlife, Fisheries, and Parks.

Ryann Campbell
Thesis Title: Prey specificity of Thanasimus dubius between latent and intermediate phases of southern pine beetle.Ryann graduated in 2011 as the Lab's first graduate. She became a sales rep for Animal Health International.

Dutton Day
Dutton was awarded a College of Agriculture and Life
Sciences/MAFES Undergraduate Research Scholarship to
conduct research on the effects of blue stain fungus on
the biodiversity of invertebrate decomposers in
Honduras, Mississippi, and Arizona. He is now pursuing a
career as a dentist at the University of Mississippi
Medical Center School of Dentistry
.

Jessica Tomasi
Jessica was awarded a College of Agriculture and Life
Sciences/MAFES Undergraduate Research Scholarship to
conduct research on the effects of blue stain fungus on
termite presence in dead wood. She then began another
2-year undergraduate research project with Dr. Mark
McConnell assessing various management practices on
native warm season grasses for northern bobwhite
quail. She is now a Farm Bill Biologist with Quail
Forever in Alabama.

Vaughn Hamill
Vaughn was awarded a College of Agriculture and Life
Sciences/MAFES Undergraduate Research Scholarship to
conduct research on assessing the use of ecoacustical
recordings to measure invertebrate diversity and
richness within logs. He is currently the lab manager
/research assistant for the Veterinary Diagnostic Lab -
Molecular R&D section at Kansas State University,
and plans on attending graduate school for
Geological/Earth/Space science.

Lauren Gamblin
Lauren was a horticulture major originally from Ohio, and was awarded a College of Agriculture and Life Sciences/MAFES Undergraduate Research Scholarship to conduct her research on phenology and community ecology of leaf litter invertebrates and their role in wood decomposition of southern forests. Additionally, she was awarded a Garden Club of America scholarship in Spring, 2015 to expand this research.Research
Multi-Discipline Approach
Ecosystem Services



Current Research Projects
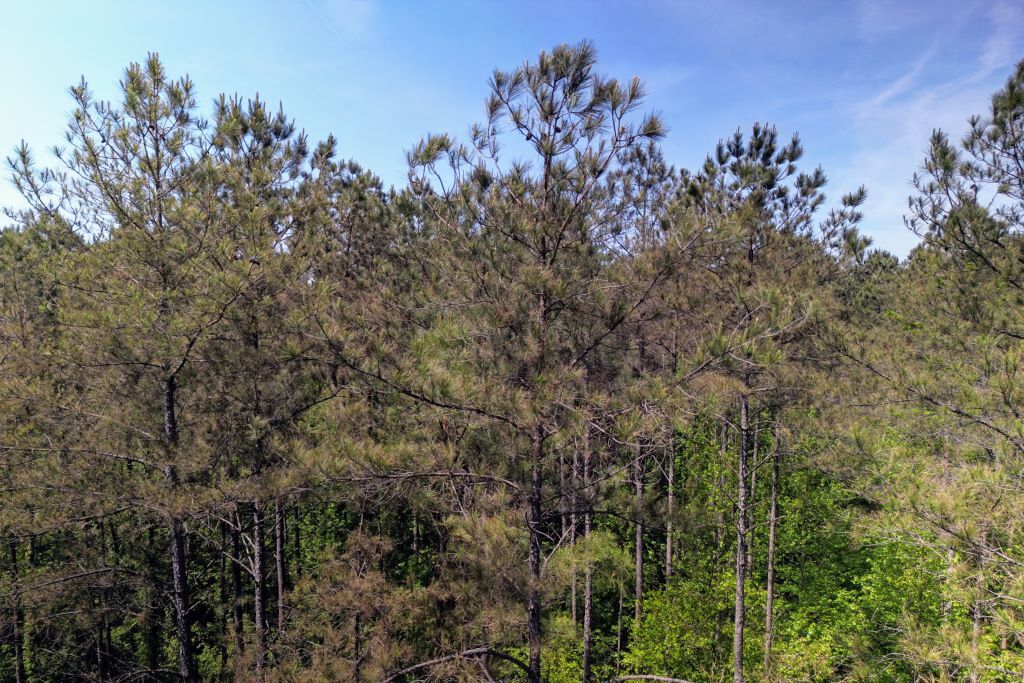

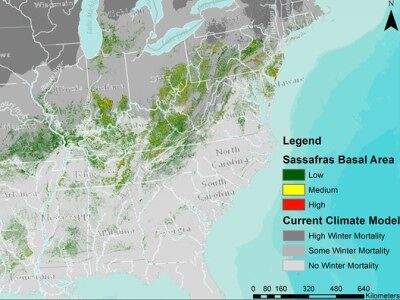
Brown Spot Needle Blight
The rapid spread of Brown Spot Needle Blight (BSNB) in Southeastern loblolly pine forests poses a significant threat to their health and productivity. This research project aims to understand and manage this emerging forest disease through a comprehensive approach, investigating its epidemiology, ecological impacts, and potential control strategies. By collaborating with foresters, landowners, and other stakeholders, we will develop effective management tools and provide crucial information to mitigate the impact of BSNB and protect the ecological and economic value of our Southeastern forests. Click here to learn more .
Arthropod Responses to Longleaf Pine Ecosystem Restoration
The restoration of longleaf pine ecosystems is crucial for preserving the unique biodiversity of the Southeastern US. However, the impact of restoration practices, such as thinning and canopy gap creation, on the diverse arthropod communities within these ecosystems remains poorly understood. This research project aims to investigate how these practices influence both insect pollinators, vital for plant reproduction, and arthropod prey species, essential food sources for threatened animals like the red-cockaded woodpecker. By studying the effects of gap size, shape, and proximity, along with thinning regimes, we will gain insights into the complex relationship between forest management and arthropod diversity. Ultimately, this research will inform restoration efforts that support both ecosystem health and the conservation of threatened species.
Pictures












Teaching
Job Opportunites
Post-Doctural Associate
Ph. D. Student
We invite you to consider joining our team in the investigation of these pathogens.
Get In Touch